








Introduction
A solenoid valve is a key component in fluid control systems, used in applications like irrigation, combustion engines, and pneumatic systems. It uses an electrical signal to activate a solenoid coil, generating a magnetic field that moves a plunger to open or close the valve. This allows for quick and precise control of fluid or gas flow, making solenoid valves essential for efficient system operation.
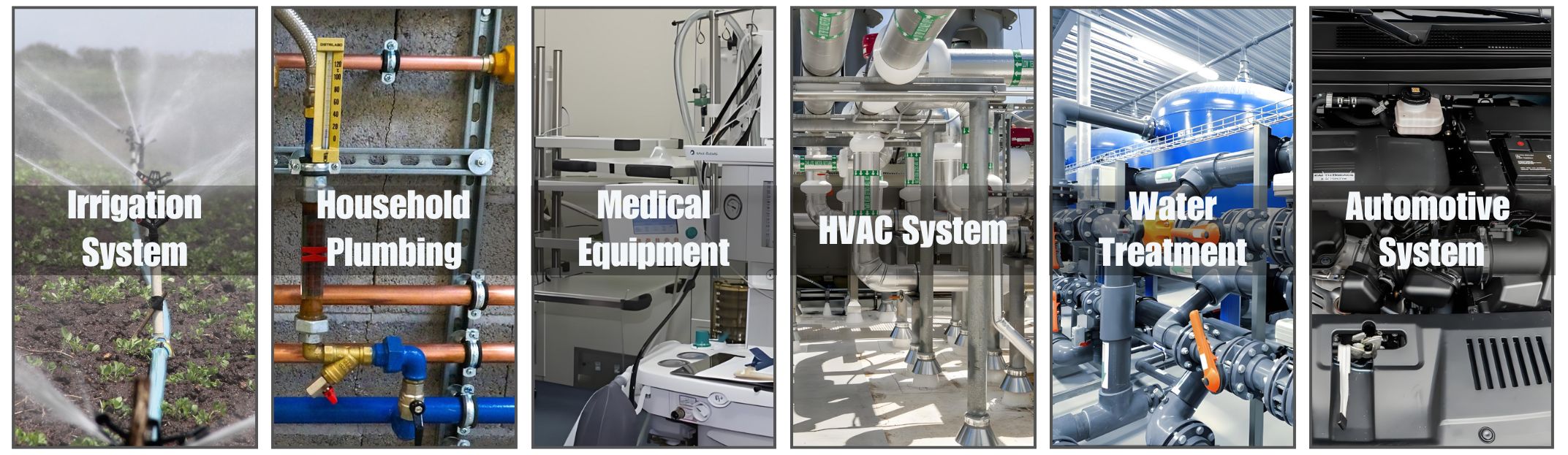
Our latest U.S. Solid semi-direct solenoid valve series has been redesigned for better efficiency, featuring a more compact design and enhanced mechanical durability. Customers chose this general purpose valve for: do-it-yourself projects, moderate temperature applications, harsh chemicals, flow control for irrigation systems, reverse osmosis systems, or to control flow of propane gas.
Applications

Features
- Normally Closed: Closed when unpowered, opens when energized.
- NPT / G Threading (3/4"): NPT (National Pipe Taper) and G (BSPP) threading to accommodate diverse global specifications, ensuring a secure seal with teflon tape.
- Valve Body Material: Constructed from robust brass. Not suitable for drinking water applications.
- Rapid Response Time: Opens/closes in under a second, with a lifespan of over a million cycles when maintained properly.
- Low-pressure Starting: Designed for low-pressure starting, this valve can operate with minimal pressure, less than 0.1 bar, ensuring versatility in low-pressure conditions.
- Viton Seal: Featuring a durable Viton seal, this valve can withstand high temperatures and resist corrosive chemicals and fluids like gasoline, oils, diesel and lubricants.
- Semi-Direct: The new series has been redesigned for improved efficiency, featuring a more compact design and enhanced mechanical durability.
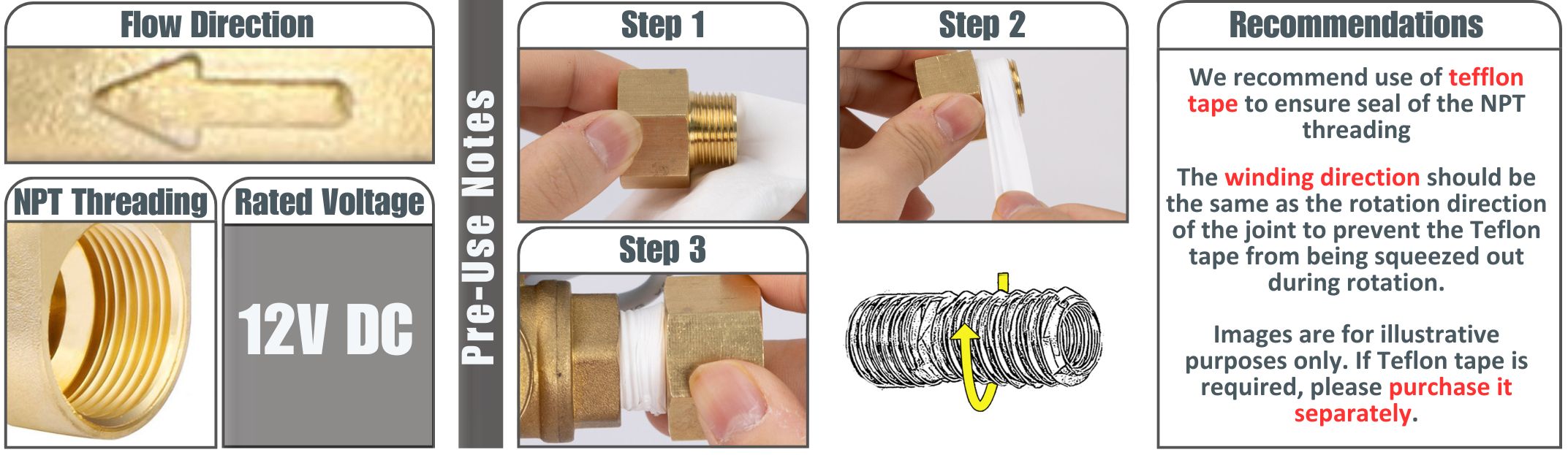

User Manual
To learn how to use this product, please refer to the user manual.
Technical Data
| Model | USS2-00059 | Port Size | 3/4" | ||
| Thread Type | NPT / G | Body Material | Brass | ||
| Operation Type | Semi-direct | Wiring Type | Lead Wire | ||
| Operation Mode | Normally Closed | Flow Aperture | 20 mm | ||
| Flow value | 7.6 Cv | Gasket/Diaphragm/Seal | Viton | ||
| Operating Time | ≤1s | Rated Voltage | DC 12V, ± 10% | ||
| IP Rating | IP65 | Power | 20 W | ||
| Operating Temperature | 14℉-248℉(-10℃-120℃) | Suitable Liquid Viscosity | 20 cst Below | ||
| Operating Pressure | Air/Water/Diesel fuel/Kerosene: 0-7 Bar (0-101 PSI); Oil: 0-5 Bar(0-72 PSI) | Suitable Media | Air, water, oil, natural gas, diesel fuel, kerosene etc. | ||
| Net Weight | 1.59 lbs | Product Dimensions | 4.40"x2.83"x2.21" | ||
*To view the full table on mobile, please swipe left or right on the screen.
Operating Principle
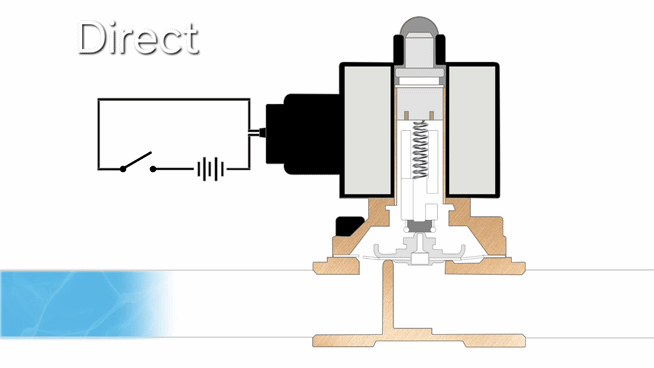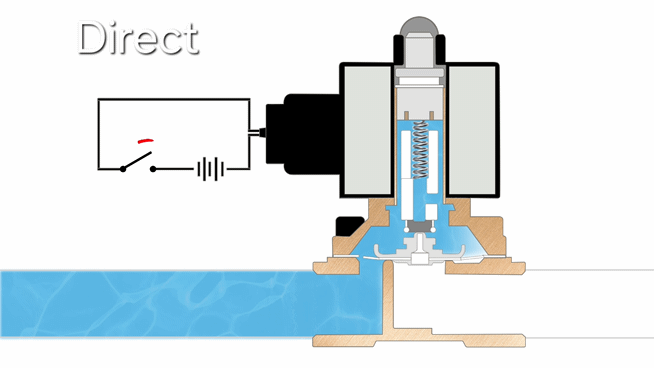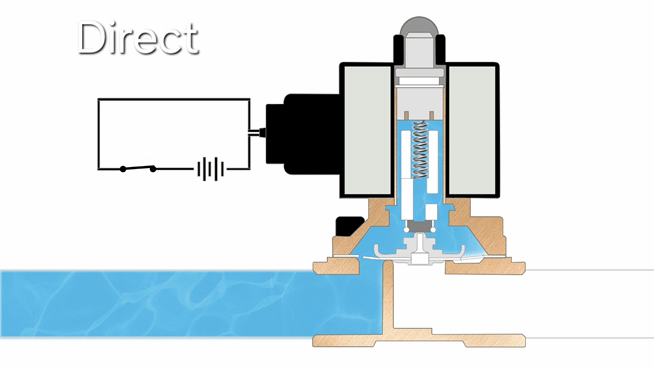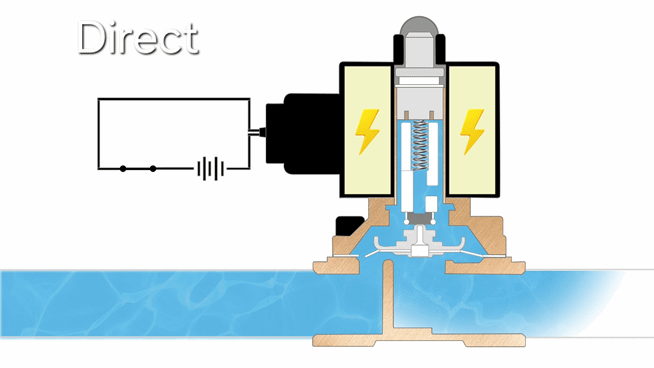
- Direct-acting solenoid valves operate by using electromagnetic force to directly lift the plunger when energized, allowing flow, with a spring returning it to closed position when de-energized. They feature simple construction and fast response, but are limited to low-pressure and small-flow applications, including vacuum systems.
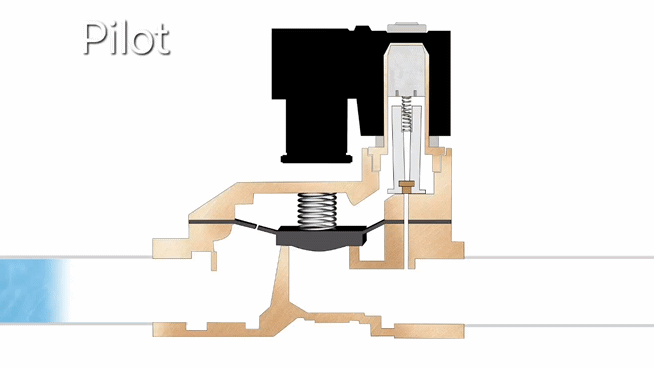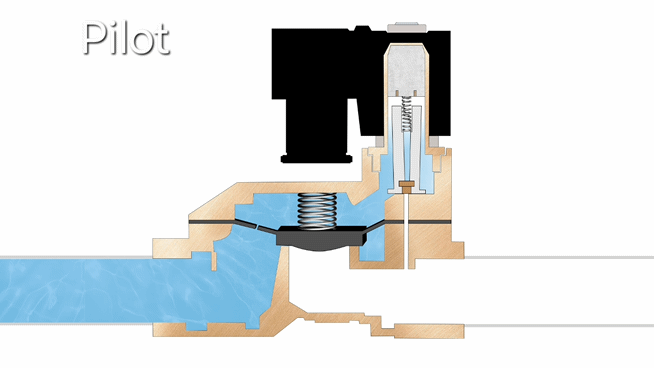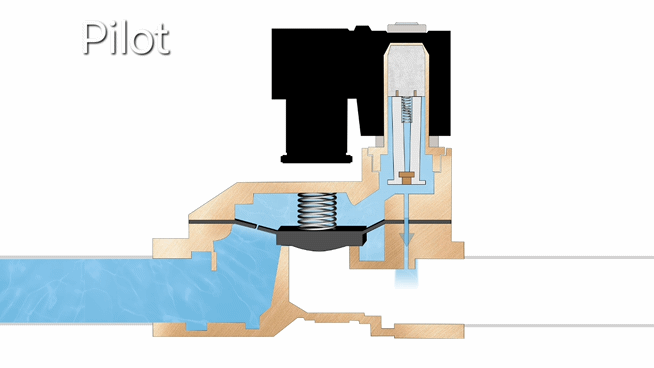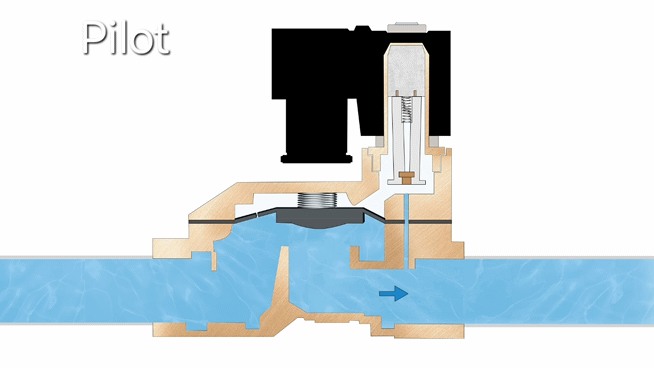
- Pilot-operated solenoid valves work by first opening a small pilot valve when energized, which then uses system pressure to operate the main valve. When de-energized, the pilot closes and the main valve resets. This design enables efficient control of high-pressure and large-flow systems with minimal power consumption, though it requires minimum operating pressure to function properly.
FAQ
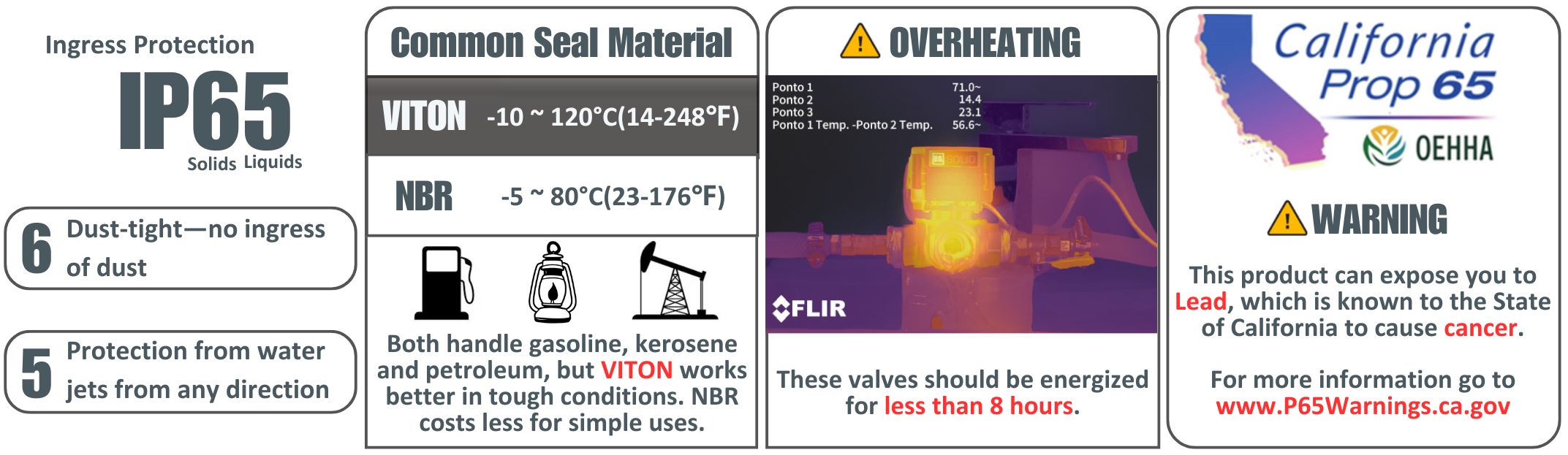
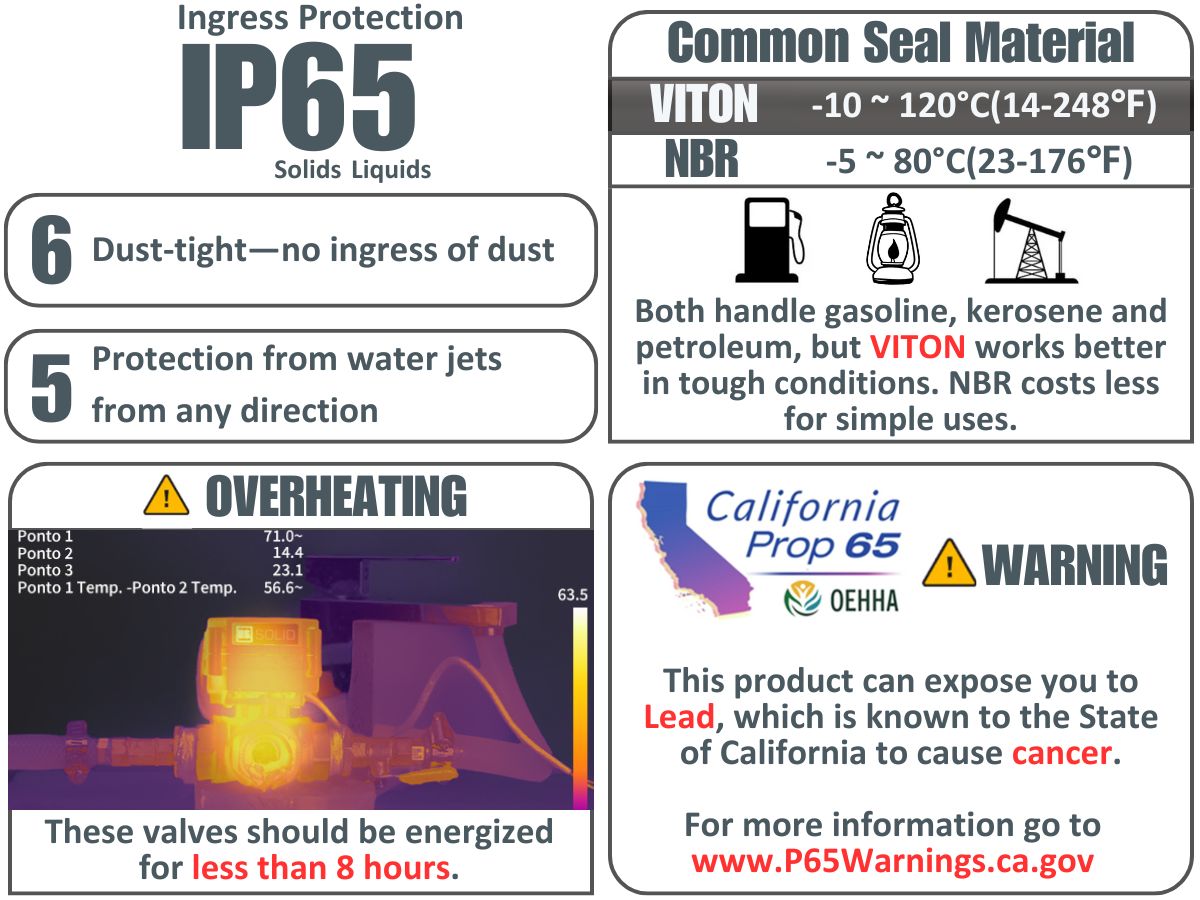
Problem 1: Which sealing material, VITON or NBR, is more suitable for use with gasoline, kerosene, or other petroleum products?
VITON. It is the better choice due to its excellent resistance to high temperatures, chemicals, and fuels. For long-term or demanding applications, VITON outperforms NBR.
Problem 2: Can these solenoid valves be used continuously for extended periods?
These valves should be energized for less than 8 hours. While most do not exceed 18W of power, the coils are in a contained area and can burn out if energized for too long. We recommend using a computer fan to keep the coil cool if continuous operation is necessary.
Problem 3: How long should you wait between two consecutive five-hour uses of our solenoid valve?
It is recommended to allow about 20 minutes of cooling time between two consecutive 5-hour operating sessions. The exact cooling time may vary depending on ambient temperature and operating conditions.
Problem 4: How long does a solenoid valve last?
With a lifespan of over a million cycles when maintained properly, the actual longevity may vary depending on factors such as operating conditions, fluid type, pressure, temperature, and maintenance practices.
Problem 5: Can this be used for Drinking Water?
NO. This solenoid valve is made of brass, which contains lead, should not be used for drinking water.
Problem 6: Can it be used outdoors?
While the solenoid valves have an IP65 rating, making them resistant to water spray, it is recommended to enclose the valve in a protective housing if permanently installed outdoors to ensure long-term durability.
Problem 7: What does the arrow on the valve body indicate?
The arrow on the valve indicates the flow direction. Most U.S. Solid valves are unidirectional, meaning they are designed to operate correctly only when fluid flows in the direction of the arrow. If installed in the opposite direction, the valve may not function properly (e.g., a Normally Closed valve may fail to close).
Problem 8: What is the difference between N.C. (Normally Closed) and N.O. (Normally Open)?
- Normally Closed (NC): Valve remains closed when power is off, opening only when energized. Ideal for fail-safe closed applications.
- Normally Open (NO): Valve remains open when power is off, closing only when energized. Ideal for fail-safe open applications.
WIRING
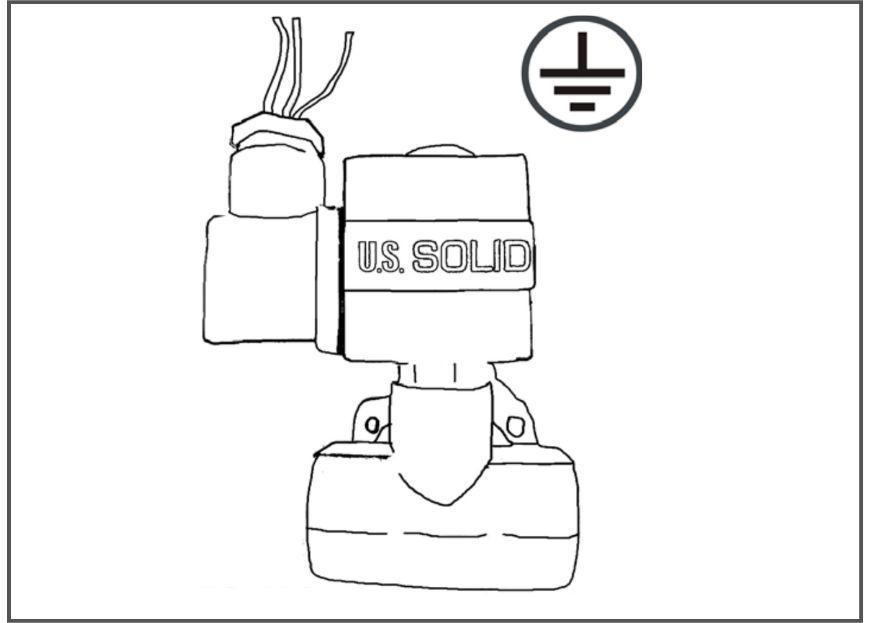
Polarity
For valves with 2 wires, the valve will actuate regardless of which terminal each wire is connected to (+ or -). Some units, like those pictured to the left, include a ground wire. Open up the connector and look for the ground symbol, shown in the corner of Figure. For valves with a ground wire, please be sure to ground the valve. For the other two wires, the valve will actuate regardless of which terminal each wire is connected to (+ or -).
Precautions
- It is recommended to filter the fluid before use to prevent impurities from blocking the valve, which could lead to incomplete closure.
- Flow Direction: During installation, ensure the arrow on the valve body aligns with the medium's flow direction. If reverse pressure is possible, install a check valve to prevent backflow.
- To ensure optimal performance and extend the solenoid valve's lifespan, install it horizontally with the coil facing vertically upward. Avoid vertical or backward coil orientation.
- The solenoid valve generates heat during operation. Avoid direct contact with your hands.
- Solenoid valves that have been out of service for an extended period should be cleaned to remove any accumulated impurities or condensation before use.
- To ensure a secure seal, always use Teflon tape when connecting NPT / G threads.
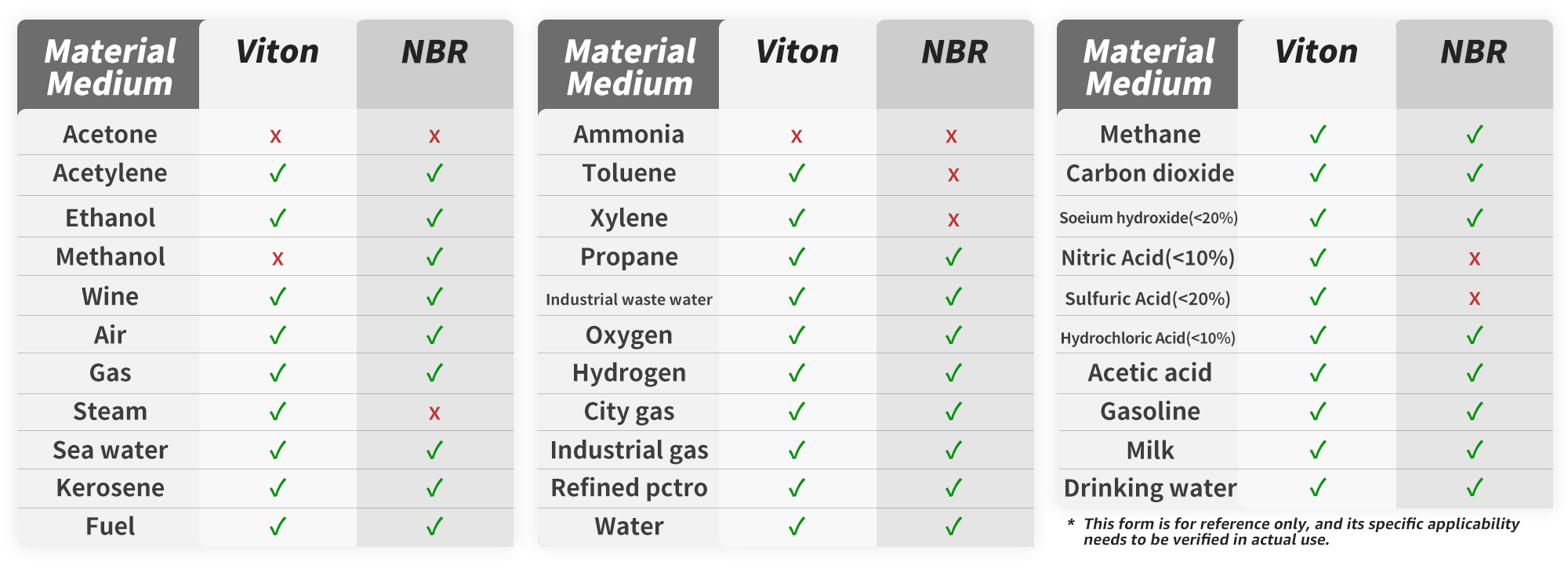
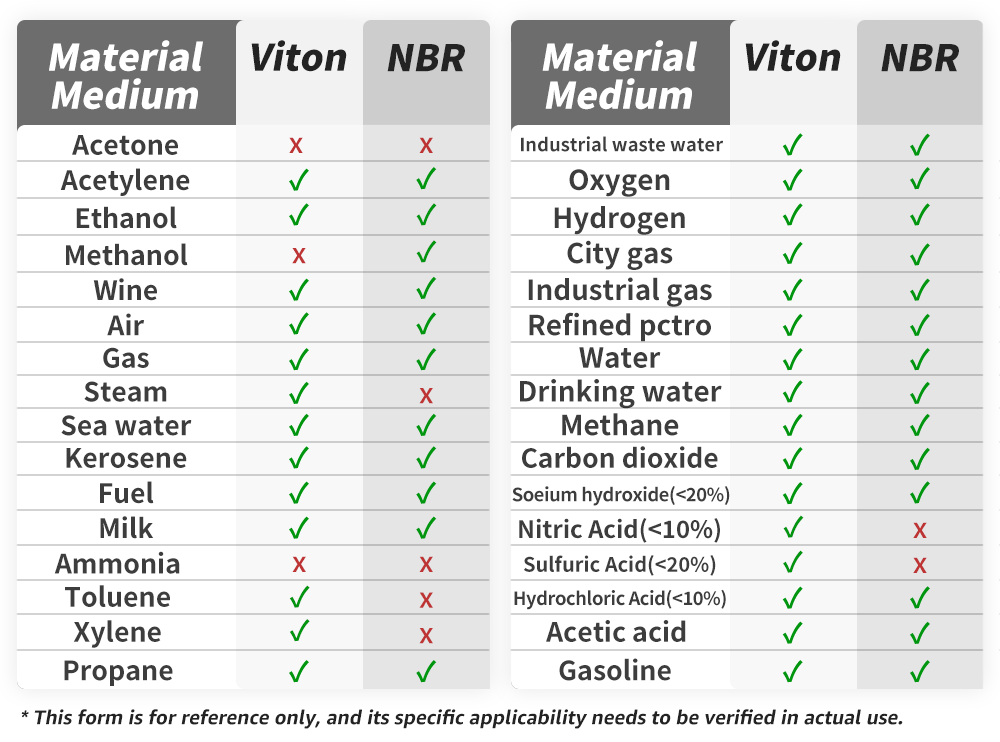
*Important: Check marks (√) denote conditional suitability only; crosses (×) indicate complete incompatibility.








