









Introduction
A solenoid valve is a key component in fluid control systems, used in applications like irrigation, combustion engines, and pneumatic systems. It uses an electrical signal to activate a solenoid coil, generating a magnetic field that moves a plunger to open or close the valve. This allows for quick and precise control of fluid or gas flow, making solenoid valves essential for efficient system operation.
This model differs from standard solenoid valves by incorporating self-holding technology. It requires only a momentary electrical pulse to switch positions and maintains its state after power removal without continuous energization. The design generates less heat and consumes significantly reduced power compared to conventional models.
With their quick response times, long service life, low energy consumption, and simple maintenance, self-holding solenoid valves are well-suited for a wide range of fluid control needs. Perfect for applications that require extended operation without constant power supply, the self-holding solenoid valve not only enhances operational efficiency but also helps lower overall energy costs.
Applications


Features
- Continuous Use: The self-holding mechanism allows the coil to maintain its position after activation, without the need for continuous power or sustained voltage.
- Junction box: Provides secure wiring protection for harsh environments (dust, moisture, vibration).
- NPT / G: NPT (National Pipe Taper) and G (BSPP) threading to accommodate diverse global specifications, ensuring a secure seal with teflon tape.
- Valve Body Material: Constructed from robust brass. Not suitable for drinking water applications.
- Rapid Response Time: The coil operates with a quick energizing time of just 30 to 50 milliseconds, ensuring a rapid response.
- Zero-pressure Startup: This valve is capable of starting at zero pressure and can withstand up to 0.5 MPa.
- Viton Seal: Featuring a durable Viton seal, this valve can withstand high temperatures and resist corrosive chemicals and fluids like gasoline, oils, diesel and lubricants.
- Direct-acting: Simple, fast-response, and works from zero pressure.



User Manual
To learn how to use this product, please refer to the user manual.
Technical Data
| Model | USS-YSV10012/USS-YSV10012-G | Port Size | 3/4" | ||
| Thread Type | NPT/G | Body Material | Brass | ||
| Operation Type | Direct | Wiring Type | Junction Box | ||
| Operation Mode | Normally Closed | Flow Aperture | 20 mm | ||
| Flow value | 3.96 m³/h | Gasket/Diaphragm/Seal | VITON | ||
| Response Time | 30-50 ms | Rated Voltage | DC 12V | ||
| IP Rating | IP65 | Power | 15W | ||
| Operating Temperature | -22℉-302℉(-30℃-150℃) | Suitable Liquid Viscosity | 20 cst Below | ||
| Operating Pressure | 0.0-0.5 MPa | Suitable Media | Air, water, diesel oil, kerosene, etc. | ||
| Net Weight | 1.52 lbs | Package Dimensions | 4.65"x3.76"x2.44" | ||
*To view the full table on mobile, please swipe left or right on the screen.
How to Wire
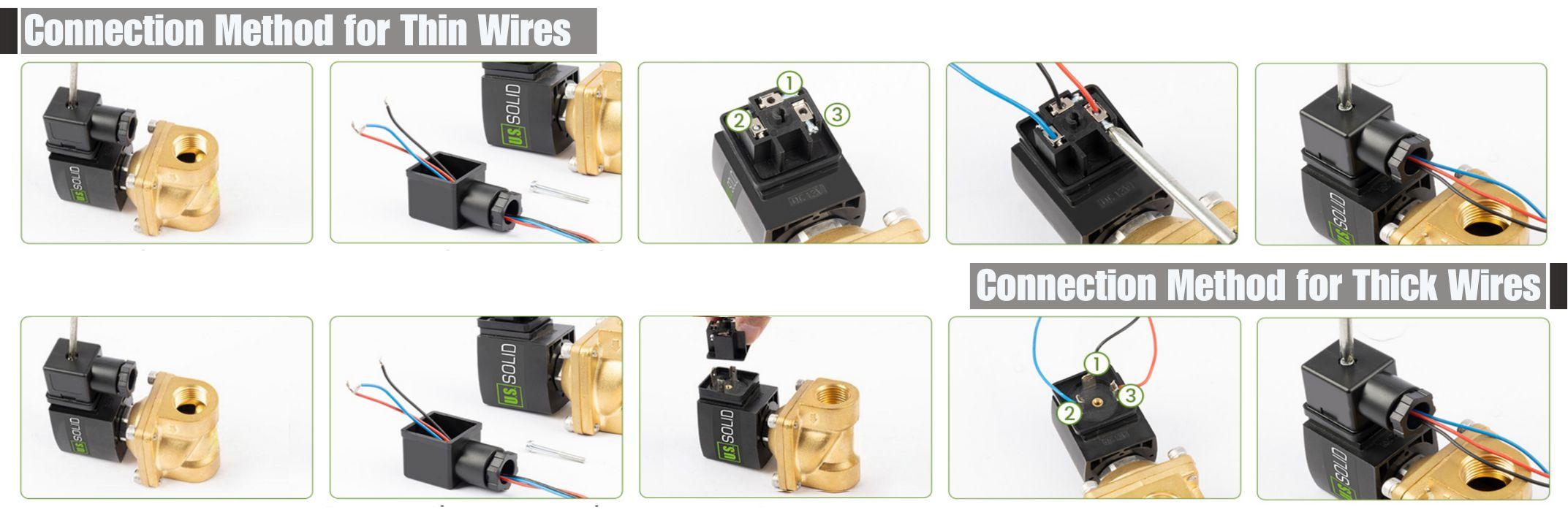



*Note: Terminal ① (top) is for the ground wire. As for terminals ② and ③ (bottom), their wiring varies according to the working state of the valve:
- In normally open working state: Connect the positive pole to the left terminal ② and the negative pole to the right terminal (the remaining one).
- In normally closed working state: Connect the negative pole to the left terminal ② and the positive pole to the right terminal (the remaining one).
*Note: The wiring diagram shown here is for demonstration purposes only. The example product may differ from the current page item.
FAQ
Problem 1: Which sealing material, VITON or NBR, is more suitable for use with gasoline, kerosene, or other petroleum products?
VITON. It is the better choice due to its excellent resistance to high temperatures, chemicals, and fuels. For long-term or demanding applications, VITON outperforms NBR.
Problem 2: Can these solenoid valves be used continuously for extended periods?
Yes, self-holding solenoid valves can be used continuously for extended periods. They maintain their state (open/closed) without continuous power after a brief activation pulse, reducing heat buildup and enabling long-term use.
Problem 3: How long does a solenoid valve last?
With a lifespan of over a million cycles when maintained properly, the actual longevity may vary depending on factors such as operating conditions, fluid type, pressure, temperature, and maintenance practices.
Problem 4: Can this be used for Drinking Water?
NO. This solenoid valve is made of brass, which contains lead, should not be used for drinking water.
Problem 5: Can it be used outdoors?
While the solenoid valves have an IP65 rating, making them resistant to water spray, it is recommended to enclose the valve in a protective housing if permanently installed outdoors to ensure long-term durability.
Problem 6: What does the arrow on the valve body indicate?
The arrow on the valve indicates the flow direction. Most U.S. Solid valves are unidirectional, meaning they are designed to operate correctly only when fluid flows in the direction of the arrow. If installed in the opposite direction, the valve may not function properly (e.g., a Normally Closed valve may fail to close).
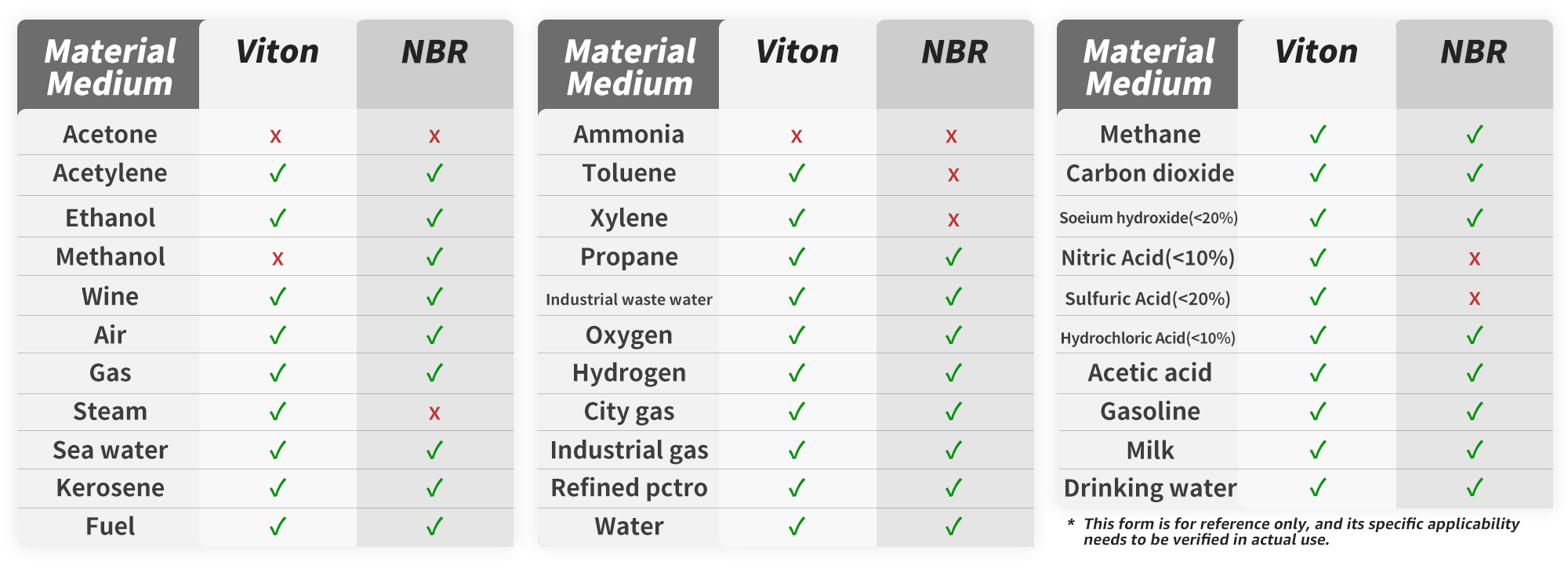
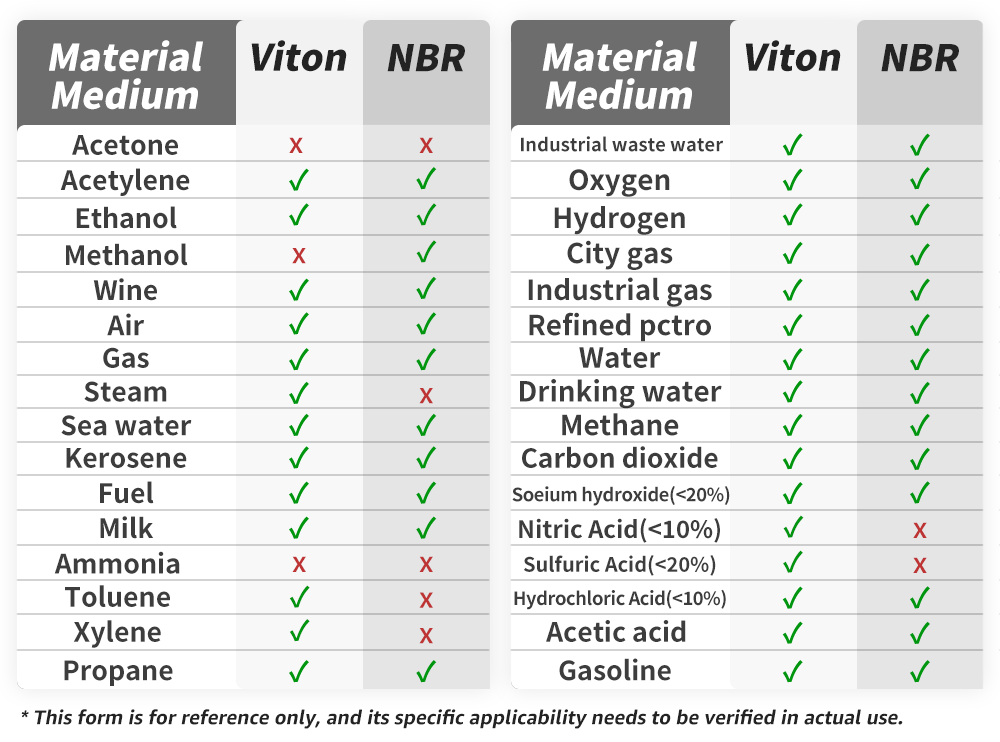
*Important: Check marks (√) denote conditional suitability only; crosses (×) indicate complete incompatibility.









